We Bee Scientists: Kindergarten: There's Ants in my Plants!

This set of units offers an in-depth look into the structure and function of the parts of ants, the difference between living and nonliving things, and explores senses and tests to see if ants response to their environment. This free, hands-on, all-inclusive curriculum set will have your students developing models, singing, acting, and learning all about the wonder of ants while meeting rigorous standards.
What’s included:
- Lesson Plans: For each of the 3 Units, you’ll have access to step-by-step lesson guides to prepare your teaching without feeling scripted. Lessons are hands-on, incorporate multiple science and engineering practices, and will have your students completely engaged!
- Worksheets: Each unit includes worksheets, assessments, and student self-assessments that you can use to evaluate student learning.
- Slide Shows: For each unit, you will also have access to a slide deck that is ready for you to present and teach with! Slides include activities, high-quality photo resources, and explanations to accompany all the exploring your students will do.
- Assessments
K.P2U1.1 Investigate how senses can detect light, sound, and vibrations even when they come from far away; use the collected evidence to develop and support an explanation. People use their senses to learn about the world around them. Their eyes detect light, their ears detect sound, and they can feel vibrations by touch. (K.P2U2.2)
K.P2U2.2 Design and evaluate a tool that helps people extend their senses. People use their senses to learn about the world around them. Their eyes detect light, their ears detect sound, and they can feel vibrations by touch. (K.P2U1.1)
K.L1U1.6 Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information about how organisms use different body parts for survival. All organisms have external parts. Different animals use their body parts in different ways to see, hear, grasp objects, protect themselves, move from place to place, and seek, find, and take in food, water, and air. Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. (K.L1U1.7)
K.L1U1.7 Observe, ask questions, and explain how specialized structures found on a variety of plants and animals (including humans) help them sense and respond to their environment. All organisms have external parts. Different animals use their body parts in different ways to see, hear, grasp objects, protect themselves, move from place to place, and seek, find, and take in food, water, and air. Plants also have different parts (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits) that help them survive, grow, and produce more plants. (K.L1U1.6) Animals have body parts that capture and convey different kinds of information needed for growth and survival — for example, eyes for light, ears for sounds, and skin for temperature or touch. Animals respond to these inputs with behaviors that help them survive (e.g., find food, run from a predator).
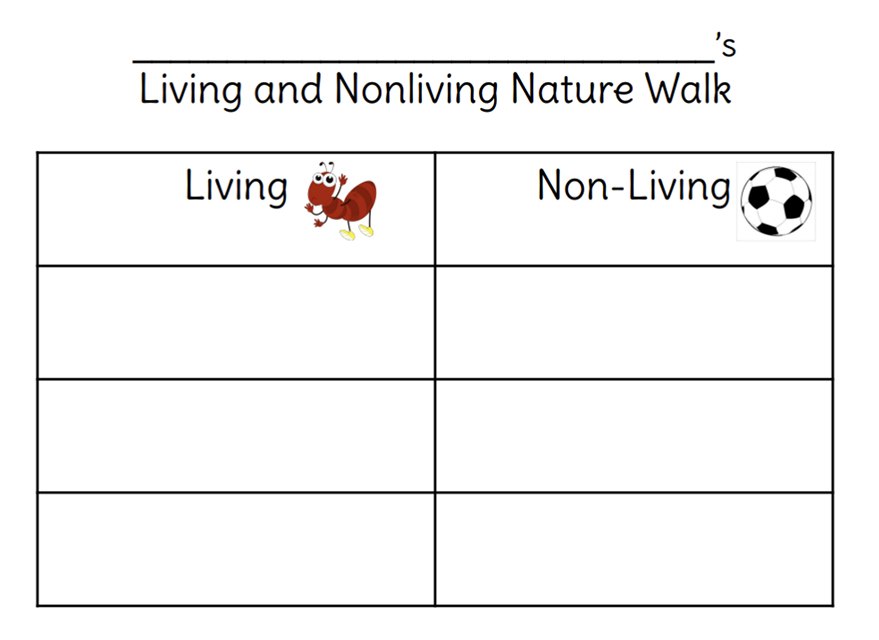
K.L2U1.8 Observe, ask questions, and explain the differences between the characteristics of living and non-living things. There is a wide variety of living things, including plants and animals. They are distinguished from non-living things by their ability to move, reproduce, and react to certain stimuli.
UNIT 1: Students will learn to determine the difference between living and nonliving things by sorting photos, taking a walk around their campus, and generate a list of living and nonliving things in their ant habitat.
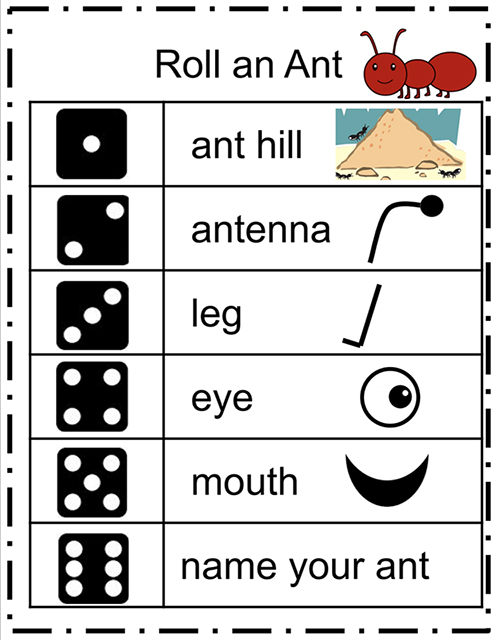
UNIT 2: Students learn that living things are made up of parts. They compare the parts of an ant to those of a human and compare the functions of those parts. Students will create a model of an ant and explain what parts make up the ant and how those parts help the ant survive.
UNIT 3: Students explore their senses and test to see if ants respond to their environment using the same sense as humans. Students will engineer a device, inspired by the ants, to extend one of their senses.
Google Classroom Code
To join our Google Classroom, sign in to your Google account. Navigate to Classrooms (either through your Google waffle or by searching Google Classrooms), and then select the plus sign in the upper right corner of your screen. Enter your Classroom Join Code nj62k57. Joining our Google Classroom allows you to communicate with us about the curriculum, and allows us to notify you of any support or updates to material we may offer.